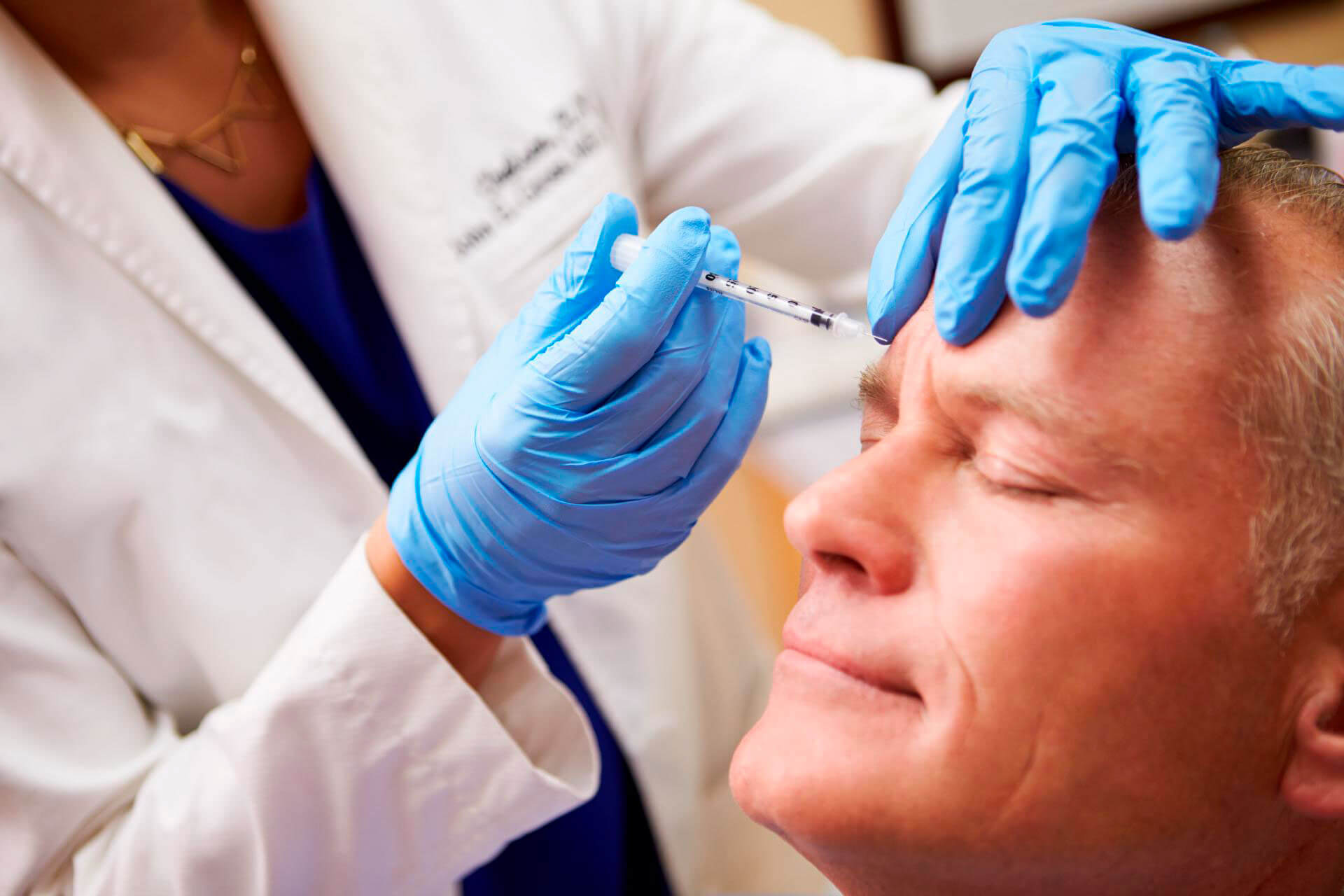
Acute cerebrovascular accident is often accompanied by increasing muscle spasticity. It develops after a stroke and may be accompanied by severe pain.
In the long term, spasticity leads to abnormal patterns of limb movement. The condition worsens the quality of life of a person, prevents him from restoring complex motor skills.
Spasticity of the muscles of the upper limbs negatively affects the social and professional life of a person, limits his household activities. Often, spasticity of one hand leads to the fact that the patient literally relearns, gets used to doing everything with one hand. This also affects the quality of rehabilitation.
Therefore, after cerebrovascular accidents, special attention is paid to rehabilitation measures, part of which may be botulinum therapy.
Mechanism of action of botulinum toxin
Botulinum toxin type A (BTA) is a neuropeptide produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. It affects the transmission of nerve impulses to the muscle, preventing its contraction.
This effect has allowed the widespread use of botulinum toxin preparations in the treatment of neurological diseases. In particular, BTA is used in rehabilitation after strokes in adults.
Botulinum therapy consists of injecting botulinum neurotoxin preparations, such as Relatox®, into the muscles.
Botulinum toxin blocks the transmission of nerve impulses to muscle tissue. At the injection site, muscle fibers stop contracting, which allows relaxation and elimination of pathological tension.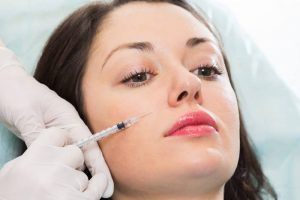
One of the indications for the use of the Russian drug Relatox® is spasticity of the muscles of the upper extremities after an ischemic stroke. The decrease in muscle hypertonicity begins after the injection, and the maximum effect is observed after a month.
The results of botulinum therapy
The use of botulinum toxin in the framework of rehabilitation allows you to get the following results:
? muscle https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skeletal_muscle relaxation;
? removal of pain associated with spasticity;
? improving opportunities for exercise therapy;
? contracture prevention.
Botulinum therapy improves the effectiveness of rehabilitation measures, makes it possible to increase the range of motion, ensure normal mobility of the joints of the upper limbs and prevent irreversible changes associated with muscle spasticity.